Introduction: The Rise of China’s Naval Strength
In the past decade, China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet has captured global attention as it signifies the country’s rapid rise as a maritime power. As tensions in the South China Sea and the broader Indo-Pacific region continue to intensify, China’s expanding naval capabilities, particularly its aircraft carrier fleet, have emerged as key components in its strategy to assert dominance and secure its interests.
By 2026, China’s fleet is expected to challenge established naval powers like the United States, fundamentally reshaping naval warfare and global power dynamics. In this article, we will explore how China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet is reshaping naval power, the technological advancements behind it, and the implications for international relations and security.
What Is an Aircraft Carrier, and Why Is It Important?
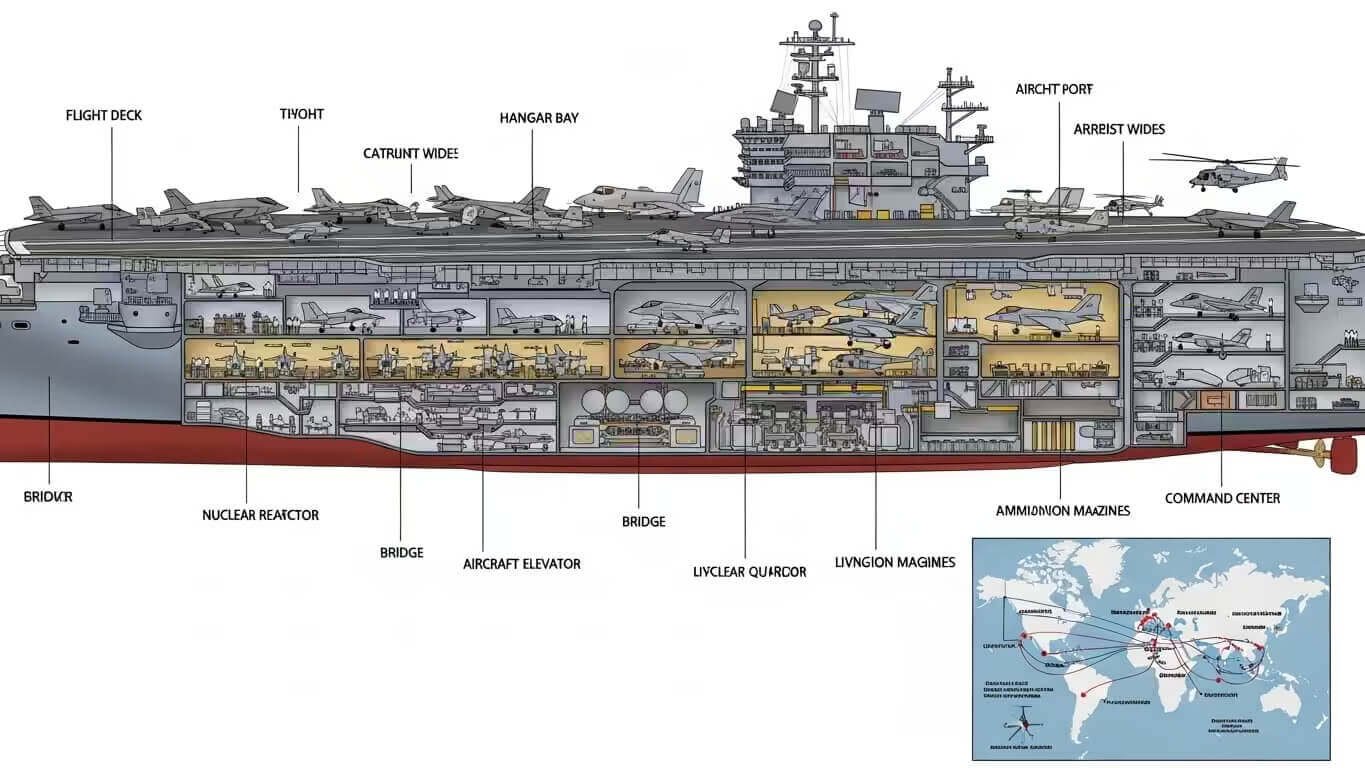
Definition of an Aircraft Carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship designed to serve as a base for aircraft, allowing for air superiority at sea. These ships can carry, deploy, and recover aircraft, and they serve as a central hub for naval operations. Aircraft carriers enable countries to project military power across vast distances, providing unparalleled mobility and flexibility.
In modern naval warfare, aircraft carriers are invaluable for:
- Power projection: Ability to deploy fighter jets and reconnaissance aircraft on long-range missions.
- Strategic deterrence: Aircraft carriers are symbols of naval strength, often used as tools for maintaining geopolitical influence.
- Combat versatility: These ships can serve as platforms for air strikes, surveillance, and even humanitarian missions in crisis zones.
The Role of Aircraft Carriers in Modern Naval Warfare
Aircraft carriers have become a cornerstone of modern naval strategies, allowing nations to project power well beyond their shores. They are essential for maintaining control over important maritime chokepoints and conducting operations such as air superiority, sea control, and rapid military response.
The Rise of China’s Aircraft Carrier Fleet
China’s Military Modernization
China’s military modernization efforts have been focused on increasing both its defensive and offensive capabilities. The expansion of China’s aircraft carrier fleet is a direct result of this effort, as the country seeks to assert dominance in the Indo-Pacific and maintain a strategic presence near contested regions like Taiwan and the South China Sea.
China’s military strategy, known as the “Anti-Access/Area Denial” (A2/AD), aims to prevent foreign intervention, particularly from the U.S., by using a mix of technologies and strategies, including aircraft carriers, missile systems, and cyber warfare. The growing aircraft carrier fleet is an essential component of this strategy, offering the ability to project power while ensuring protection of its maritime interests.
China’s First Aircraft Carrier: Liaoning (CV-16)
China’s journey to becoming a major naval power began with the acquisition and refurbishment of the Liaoning (CV-16), its first aircraft carrier. Originally built by the Soviet Union as the Varyag, China purchased and completed the vessel in 2012. Although not as advanced as modern U.S. carriers, the Liaoning served as an important platform for China to develop its naval aviation capabilities.
Shandong (CV-17): China’s Second Aircraft Carrier
China’s second aircraft carrier, the Shandong (CV-17), was launched in 2017, and it represents a significant step forward in China’s aircraft carrier capabilities. The Shandong is a Liaoning-class carrier, but it has been designed with improvements in terms of design, systems, and equipment. It also represents China’s ambition to develop its own domestic aircraft carrier program, featuring a ski-jump ramp for launching aircraft.
The Technological Advancements Behind China’s Growing Aircraft Carrier Fleet
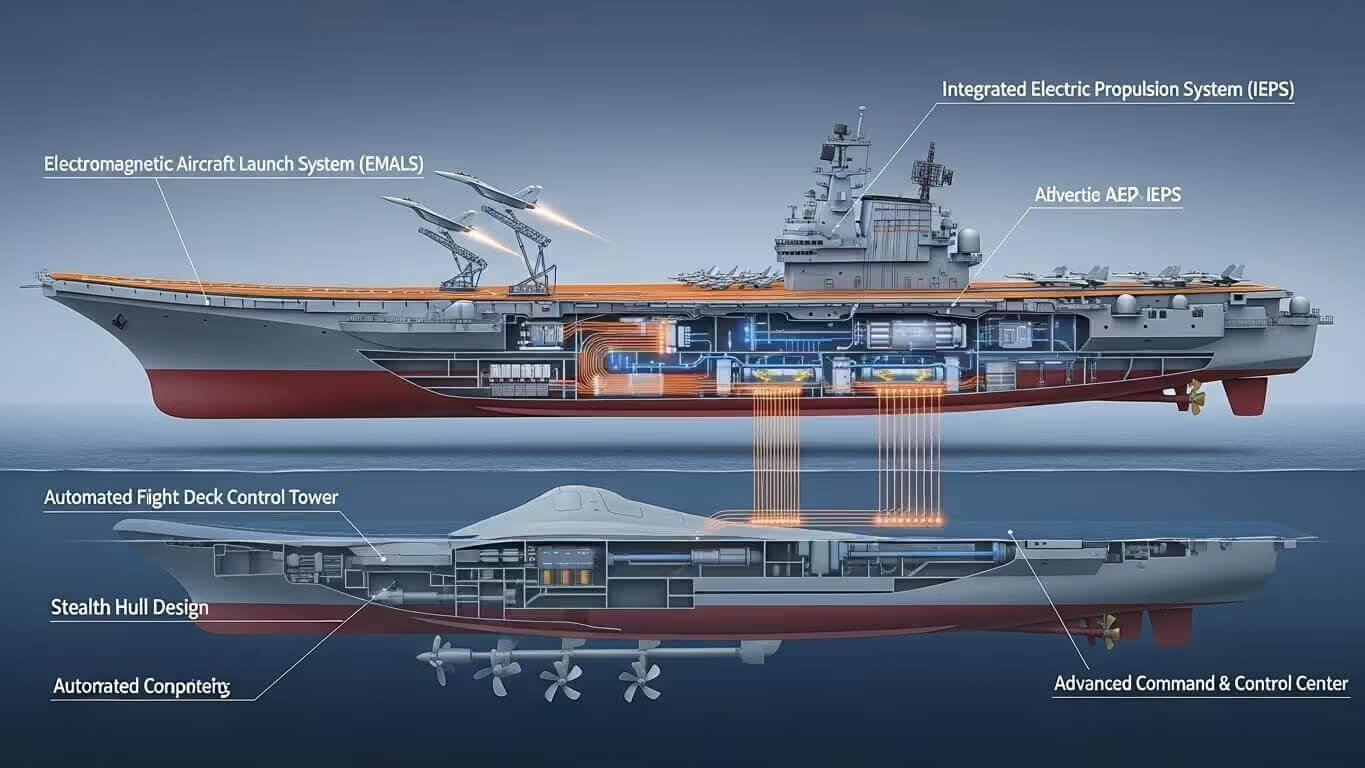
Design and Capabilities of China’s Aircraft Carriers
China’s aircraft carriers are equipped with modern technologies that allow them to operate effectively in hostile environments. The Liaoning and Shandong are both ski-jump carriers, a design more commonly used by nations like the U.K. and Russia. This allows for short takeoff and landing (STOBAR) aircraft operations, which are essential for launching aircraft from a confined space.
However, China’s future carriers, such as the Type 003 (currently under construction), are expected to feature electromagnetic catapults, similar to those used by U.S. carriers. These catapults will allow China’s carriers to launch heavier aircraft and operate more efficiently, further enhancing their ability to project force.
Carrier-Based Aircraft: J-15 Fighter Jet
One of the standout features of China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet is the J-15 fighter jet, which operates from both the Liaoning and Shandong. The J-15, often referred to as the “Flying Shark,” is a carrier-based multirole fighter, designed to carry out a variety of missions including air superiority, strike operations, and reconnaissance.
Despite some early challenges, the J-15 has improved over time and is expected to play a critical role in China’s naval air force. Additionally, China is working on developing newer carrier-based aircraft such as the J-35, a stealth fighter designed to operate from China’s future carriers.
China’s Aircraft Carrier Fleet in Numbers
China’s aircraft carrier fleet is expected to continue expanding. With the addition of new carriers like the Type 003, China’s fleet will likely rival that of other major naval powers. By 2030, estimates suggest that China will possess at least four aircraft carriers, including the Type 003 and possibly others based on nuclear power.
Implications of China’s Growing Aircraft Carrier Fleet

Strategic Impact on Global Power Dynamics
The expansion of China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet is reshaping the global balance of power. As China builds more advanced carriers, it strengthens its ability to challenge the United States and its allies, especially in the Indo-Pacific. The presence of a powerful Chinese fleet complicates maritime operations for the U.S. and its partners, making it harder to maintain freedom of navigation in the South China Sea and East China Sea.
The United States’ dominance in naval power is being increasingly challenged as China builds a fleet capable of projecting power over vast distances. This shift could lead to a new era of naval rivalry, particularly as both nations invest in advanced naval technologies, including nuclear-powered vessels and advanced missile systems.
Increased Tensions in the South China Sea and Taiwan Strait
The strategic importance of China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet cannot be understated, particularly in the context of the South China Sea and the Taiwan Strait. These regions have been sources of ongoing conflict and territorial disputes, with several countries claiming ownership of various islands and maritime zones.
The addition of more aircraft carriers allows China to maintain a significant presence in these areas, asserting its claims and ensuring that foreign intervention is deterred. This growing military presence also complicates international relations, particularly with the United States, Japan, and Southeast Asian nations.
The Military Implications for the United States Navy
For the U.S. Navy, China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet presents a direct challenge to its dominance in the Indo-Pacific. The U.S. has long maintained a military presence in the region, relying on aircraft carriers like the USS Ronald Reagan and the USS Nimitz. However, as China expands its fleet, the United States will need to adapt to counter the evolving threat.
This could involve increasing investments in newer, more advanced aircraft carriers, as well as enhancing its missile defense systems and naval aircraft to match the growing capabilities of China’s fleet.
China’s Aircraft Carrier Fleet: The Future Outlook
The Type 003 Aircraft Carrier: China’s Next-Generation Ship
The Type 003 is China’s most advanced aircraft carrier, expected to enter service by the early 2030s. This carrier will feature electromagnetic catapults, which will allow for faster and more efficient aircraft launches compared to the older ski-jump designs. Additionally, it will likely carry a larger complement of aircraft, including advanced fighter jets, surveillance planes, and drone systems.
The Type 003 represents the future of China’s naval power, and its introduction will significantly enhance the country’s ability to project power across the Pacific and beyond.
The Potential of Nuclear-Powered Carriers
In the long term, China may also develop nuclear-powered aircraft carriers, similar to the U.S. Nimitz-class and Ford-class carriers. Nuclear propulsion would allow for longer operational periods without the need for frequent refueling, giving China’s navy a significant operational advantage in the region.
Global Naval Rivalry: A New Arms Race?
As China continues to expand its aircraft carrier fleet, it raises the question of whether a new naval arms race is emerging. The growing focus on aircraft carriers and other advanced naval assets suggests that more countries will prioritize naval power as a key component of their military strategy.
Conclusion: A New Era of Naval Power
China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet is more than just a symbol of power; it represents a significant shift in the global balance of naval forces. With advanced designs, cutting-edge technology, and a clear strategic focus on power projection, China is positioning itself as a dominant maritime force. As the world watches, the expansion of China’s carrier fleet will undoubtedly have profound implications for global security, military strategy, and geopolitical relations.
FAQs
1. What is the significance of China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet?
China’s expanding aircraft carrier fleet allows it to project power across the Indo-Pacific, challenging the naval dominance of the United States and enhancing its military presence in critical regions.
2. How many aircraft carriers does China have currently?
As of 2026, China has two operational aircraft carriers, Liaoning and Shandong, with a third carrier, the Type 003, under construction.
3. What are the key features of China’s aircraft carriers?
China’s aircraft carriers feature advanced technologies, including ski-jump ramps for launching aircraft and plans for the Type 003 to feature electromagnetic catapults for improved efficiency.
4. How does China’s growing fleet affect global naval power?
China’s growing aircraft carrier fleet challenges the dominance of the U.S. Navy, particularly in the Indo-Pacific region, and could shift the balance of naval power in the coming decades.
5. What is the future of China’s aircraft carrier fleet?
The future of China’s aircraft carrier fleet includes the introduction of the Type 003, featuring advanced technology like electromagnetic catapults, and the potential development of nuclear-powered carriers.
